Program Snapshot
The goal of the Common Fund’s Structural Biology program was to develop novel methods to isolate large amounts of membrane proteins and determine their protein structures.
The program provided the following resources to the scientific community:
- Laboratory Methods
- Research Tools
- Reference Materials
- Database/Libraries
During the first phase of the Structural Biology Research Program (FY2004-2008), the Common Fund supported two Centers for Innovation in Membrane Protein Production that enabled interdisciplinary groups of scientists to develop innovative methods for producing large quantities of membrane proteins. In addition, a number of small exploratory (R21) and regular research (R01) grants were awarded to individual investigators to broaden the base of innovative ideas under development.
During the second phase of the Structural Biology Research Program (FY2009-2013), researchers developed additional innovative approaches for membrane protein production as well as structure determination, including methodologies that can be applied to protein complexes made up of multiple protein components, such as different types of proteins. The work during this phase occurred at the two Centers for Innovation in Membrane Protein Production as well as through additional R01 grants.
Highlights of the Structural Biology program's major accomplishments are:
- Numerous scientific advances addressing complex challenges in biomedical research (see examples on the Program Highlights page)
- Dr. Brian Kobilka, grantee of the Structural Biology program, was awarded the 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for groundbreaking studies on G-protein coupled receptors (work performed in part through support of this program)
- Dr. Ray Stevens, supported by the Structural Biology program, characterized hundreds of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) membrane protein structures
Please note that since the Structural Biology program is no longer supported by the Common Fund, the program website is being maintained as an archive and will not be updated on a regular basis.
For more information on the Structural Biology Program, please contact Dr. Peter C. Preusch ([email protected]) or Dr. Jean Chin ([email protected]).
G Protein Coupled Receptor (GPCR)
G Protein Coupled Receptor (GPCR) structures solved to date through the Joint Center for Integral Membrane Protein Technologies-Complexes (JCIMPT-Complexes) 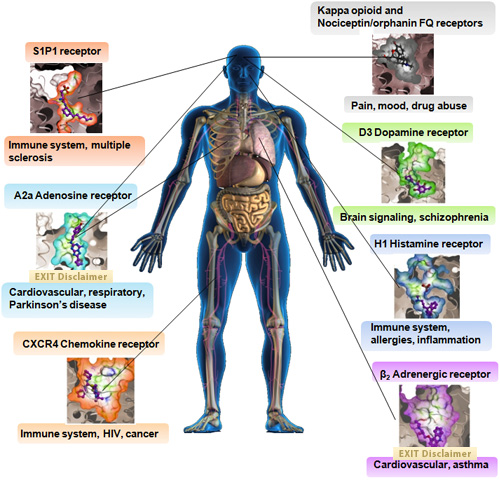
Click on the protein structure images to learn more!
In 2007, Common Fund support of pioneering methods in membrane protein production resulted in the determination of the structure of the β2 Adrenergic receptor. Since then, these methods and others have rapidly accelerated GPCR membrane protein structure determination, as shown above.
Why Care About GPCRs?
Announcements
The Structural Biology program has transitioned from Common Fund support. Common Fund programs are strategic investments that aim to achieve a set of high impact goals within a 5-10 year timeframe. At the conclusion of each program, deliverables transition to other sources of support or use within the scientific community.
The Structural Biology program was supported by the Common Fund FY2004 through FY2013. Efforts in the area of structural biology will continue via various other means of funding outside of the Common Fund.



