Health Relevance
Metabolomics is the scientific study of the chemical reactions that occur in organisms, cells, or tissues. Each reaction produces small chemicals called metabolites, which play critical roles in keeping our cells healthy and functioning properly. For example, our cells break down the food we eat into metabolites, such as sugars, amino acids, or fats, and use these metabolites for energy to power our bodies. These same metabolites derived from our food can also be used to build new cellular structures and machinery. Our cells can also break down other materials into metabolites, sometimes even parts of the cell itself, which can be used to communicate with neighboring cells and send messages all throughout the body. The sum total of all of the metabolites in our bodies is referred to as our metabolome.
Our metabolism is impacted by a variety of different factors, such as diet, genetic history, the environment, and daily activity. The Metabolomics program aims to increase our understanding of how such factors can change a person’s metabolome. In addition to increasing our understanding of how cells work, metabolomics plays an important role in our understanding of how diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer's disease, and diabetes can affect our bodies. Since every chemical reaction leaves a chemical fingerprint of the metabolites produced, researchers can use this information to find key changes that occur in disease states. This information can then be used to help develop treatments.
Metabolomics is a powerful and emerging field that allows scientists to track the unique fingerprints of chemical reactions in our bodies. Every chemical reaction produces different metabolites, and researchers can use this information to track human health. However, the study of metabolomics has remained a relatively specialized field thus far. The Common Fund’s Metabolomics program aims to expand the capacity of researchers to study metabolomics, which is expected to catalyze this important research area and accelerate progress towards harnessing the power of metabolomics to improve human health.
The Metabolomics program was started in 2012 and is anticipated to wrap up a highly successful first stage of funding later this year. During this stage, the Metabolomics program accomplished the following goals:
- Develop six Metabolomics resource cores around the country to help scientists include metabolomics in their research
- Support many different training opportunities to teach scientists how to do their own metabolomics research
- Support the development of new tools and technology to make metabolomics more accessible to scientists
- Help develop national and international standards for metabolomics data quality, storage, and usage
- Support the development of new ways to identify unknown metabolite
Due to the success of the first stage of the Metabolomics program, the NIH has continued the program into a second stage of funding, which is anticipated to start next year. During the second stage, the Metabolomics program aims to support research in the following areas:
- Support a national data repository where researchers can store, or download, metabolomics data
- Support the development of new computational tools to make the analysis of metabolomics data more user friendly
- Support the development of new, innovative ways to better identify unknown metabolites
- Promote community engagement to develop best practices for such things as metabolite naming, data usage, and detection methods.
This investment by the Common Fund's Metabolomics program will help researchers across the world use these powerful tools in their studies. By increasing the usability of existing metabolomics data, creating better tools for data analysis, helping uncover the identities of unknown metabolites, and promoting the use of standard methods, the Metabolomics program strives to create new and exciting ways to diagnose, treat, or potentially prevent many of the common diseases that impact human health.
Make sure to check out the highlights section on the website to see exciting new advancements in the metabolomics field!
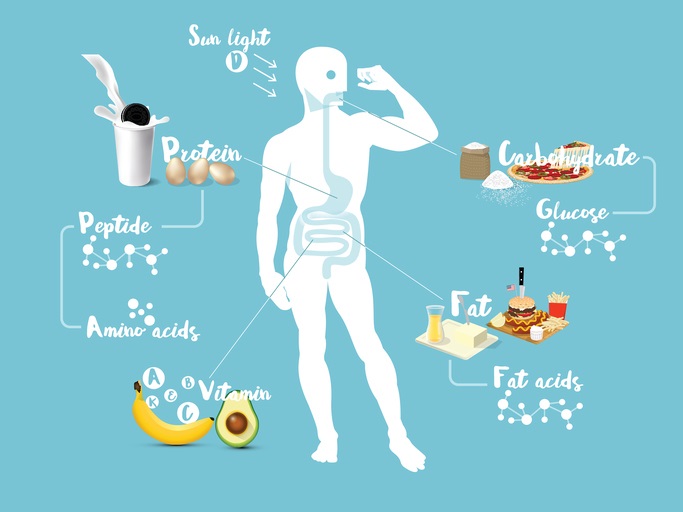
This image shows how different external sources, such as food or sunlight, can be broken down in our bodies to different metabolites, such as amino acids, sugars, and vitamins.



